Overview
Jobs have to be part of the respective workflow. They are submitted via sbatch
to the Slurm workload manager.
The order of job submission is based on the list given in workflows.yaml
(or in config.yaml in case a custom, user-defined workflow is used.)
Let’s have a look at the icon-art example:
icon-art:
features:
- restart
jobs:
- prepare_icon
- icontools
- prepare_art
- icon
This workflow consists of four jobs: prepare_icon, icontools,
prepare_art and icon.
These jobs will be submitted, however, they are not starting at the same time, because some of them depend on others:
dependencies:
icontools:
current:
- prepare_icon
prepare_art:
current:
- icontools
icon:
current:
- prepare_icon
- icontools
- prepare_art
previous:
- icon
Since icontools depends on prepare_icon, and prepare_art depends
on icontools, the order of execution is prepare_icon –> icontools
–> prepare_art. Note that if we had another job in there without dependencies,
it would run in parallel to the others.
Since icon depends on all other jobs, it will be executed last. Note that
these dependencies are all listed under the current keyword, targeting
the current chunk. For icon, there is an additional previous keyword.
This means that an icon simulation will always wait until the simulation
from the last chunk is finished (because the restart file has to be available).
Another effect of this workflow definition is that the prepare_icon,
icontools and prepare_art jobs will also be launched for the next chunk,
as they are not dependent on their previous ones.
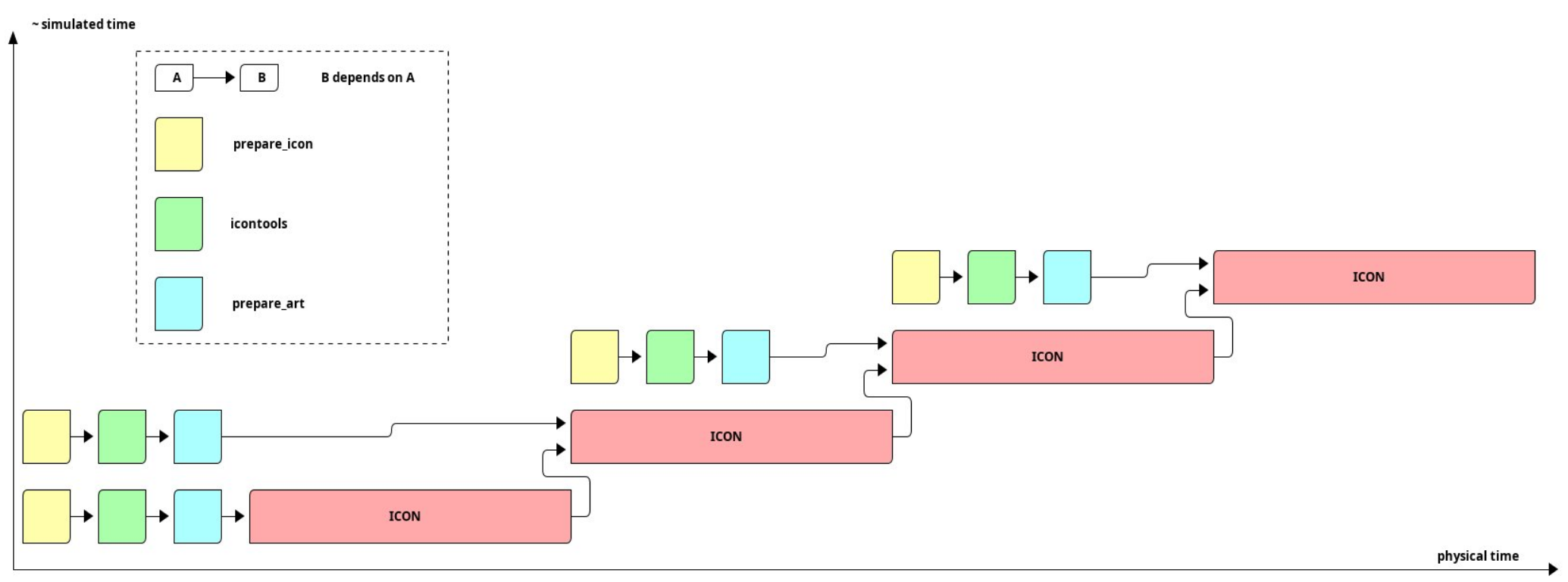
Flowchart for the icon-art workflow.
Adding New Jobs
Adding a new job to the chain is simple:
In the directory
jobs/, create a file called<jobname>.pycontaining a function calledmainwhich takes the same arguments as every other job. Make sure the function is documented with a docstring.Import it in
jobs/__init__.pyto make it accessible torun_chain.py.Add the job to your workflow.